Why Do Businesses Choose Die Casting Molds for Production?
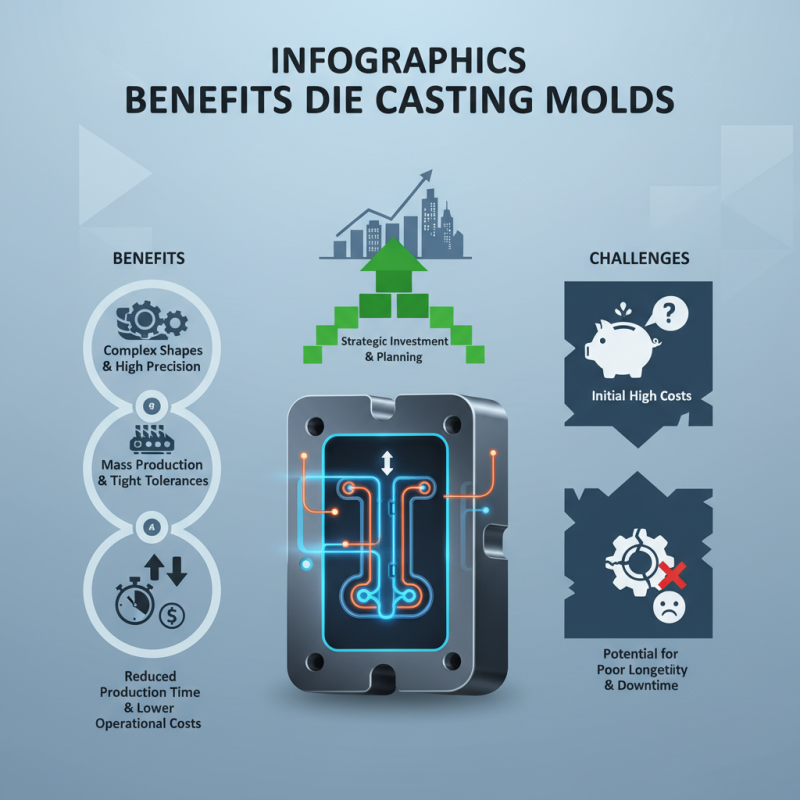
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, businesses are continually seeking efficient methods for production. Die Casting Molds have emerged as a preferred choice due to their ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the die casting market is projected to reach $19.3 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing reliance on this technology.
Die Casting Molds facilitate mass production while maintaining tight tolerances. This enables manufacturers to meet increasing consumer demands swiftly. However, there are challenges. The initial costs for creating high-quality molds can be significant. Some businesses may hesitate, facing budget constraints or concerns about return on investment. Yet, with proper planning, the benefits often outweigh these concerns.
Efficiency is key. Utilizing Die Casting Molds can reduce production time significantly. This translates to lower operational costs and increased output. However, companies must also consider the longevity of the molds. A poorly designed mold can lead to frequent breakdowns, resulting in unexpected downtime. Therefore, investing in high-quality die casting solutions is critical for success in modern manufacturing.
Understanding Die Casting: Definition and Process Overview
Die casting is a manufacturing process that utilizes molten metal. This technique is vital in producing complex shapes with high precision. It involves injecting metal into molds at high speeds and pressures. The result is a strong, durable product that meets rigorous standards. Industry reports show that die casting accounts for about 20% of total metal production in the U.S. This statistic highlights its importance in various sectors.
Despite its advantages, die casting has challenges. The initial cost of molds can be significant, often exceeding $100,000. This high investment can deter small businesses. Additionally, the process requires careful temperature control. If not managed well, it can lead to defects in the final product. A study revealed that up to 10% of die-cast parts may fail quality inspections. Such imperfections can increase costs and delay production.
Moreover, the environmental impact is a topic of concern. The energy consumption in die casting is substantial. Reports suggest that the aluminum die casting industry alone consumes over 5,000 GWh annually. This raises questions about sustainable practices in manufacturing. Companies must weigh the benefits against these potential drawbacks. It's a balance that requires continuous reflection and improvement.
Key Advantages of Die Casting Molds in Manufacturing Industries
Die casting molds offer several key advantages that make them a preferred choice in manufacturing. One important benefit is their ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global die casting market is projected to reach $79.30 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the efficiency die casting provides in maintaining consistency across large production runs.
Additionally, the use of die casting molds significantly reduces material waste. The process allows for near-net shape casting, meaning less trimming and finishing. A study from the Aluminum Association states that die casting can achieve a material utilization rate of up to 90%. This increase in efficiency not only helps in reducing costs but also in minimizing the environmental impact.
However, some may argue that the initial costs for die casting molds can be high. With custom designs and machining, these expenses can deter smaller businesses. Nonetheless, the long-term savings on production and material can outweigh this upfront investment. Companies must evaluate their needs carefully. Balancing cost and efficiency is crucial in deciding the best manufacturing process.
Advantages of Die Casting Molds in Manufacturing
This chart illustrates the key advantages of die casting molds used in the manufacturing industry. The data highlights various benefits and their relative impact on production efficiency.
Comparative Analysis: Die Casting vs. Other Metal Fabrication Methods
Die casting is a popular method for metal fabrication, especially for large-scale production. Compared to methods like machining and forging, die casting offers several advantages. It provides excellent dimensional accuracy, often up to ±0.005 inches. This precision reduces the need for extensive post-processing, saving time and cost.
Other techniques have their own strengths. Machining delivers exceptional surface finish and allows for diverse material options. However, this method can be time-consuming and expensive for large runs. Forging is robust and often results in a stronger product. Yet, the process may require more material and can have higher upfront costs.
Tips: Consider project requirements carefully. Choose die casting for high-volume production where speed and precision are crucial. Reflect on potential limitations too. Die casting works best with non-ferrous metals, which may limit material selection. Lastly, keep in mind that while die casting is efficient, the initial mold cost can be high, affecting budget decisions. These elements should guide your choice in metal fabrication methods.
Applications of Die Casting in Various Sectors and Their Importance
Die casting is a vital process in various industries. Its popularity stems from efficiency and precision. Many sectors rely on die casting to create durable parts. From automotive to electronics, die casting plays a crucial role.
In the automotive sector, die casting shapes key components. It produces engine blocks, transmission cases, and more. These parts must endure intense conditions, making durability essential. Die casting allows for complex shapes, reducing assembly time. The ability to create intricate designs helps manufacturers meet demands effectively.
Electronics manufacturers also benefit from die casting. Heat sinks and housings made through this method improve product performance. Strong, lightweight materials are vital in this sector. However, businesses must consider the environmental impact of die casting. Choosing sustainable practices can be challenging but necessary. Balancing efficiency with eco-friendly solutions is a crucial reflection point for manufacturers.
Why Do Businesses Choose Die Casting Molds for Production? - Applications of Die Casting in Various Sectors and Their Importance
| Sector | Applications | Advantages of Die Casting | Common Materials Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, transmission cases | High precision, lightweight parts | Aluminum, Zinc |
| Aerospace | Structural components, fittings | Durability, complex geometries | Titanium, Magnesium |
| Electronics | Casing, heat sinks | Thermal efficiency, intricate designs | Aluminum, Zinc |
| Consumer Goods | Household appliances, tools | Cost-effective production, aesthetic finish | Aluminum, Magnesium |
| Industrial Equipment | Machinery parts, housings | High strength, reduced weight | Zinc, Aluminum |
Challenges and Considerations in Using Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds are popular in production due to their efficiency. However, several challenges come with their use. First, the initial cost can be a barrier. Molds are expensive to create. They require precise design and high-quality materials. This investment may overwhelm small businesses.
Another consideration is the complexity of the mold design. Designing a mold is not a straightforward task. Even minor errors can lead to significant production issues. This could result in wasted metal and time. Manufacturers must invest time in prototyping and testing. Finding the right balance between design and functionality is crucial.
Lastly, maintenance poses a constant challenge. Die casting molds endure wear and tear over time. Regular maintenance is essential to extend their lifespan. Failing to do so can lead to defects in the final product. The need for constant vigilance adds pressure on manufacturers. Balancing costs and quality may require tough decisions.

